Put yourself in the shoes of a buyer. You’re looking to buy some new software. One of the potential vendors subscribes to the MEDDIC sales methodology. You schedule a call, and during the call, the sellers asks you a series of questions:
- What is the economic impact of the solution?
- Who has profit and loss responsibility for this?
- What are the technical, vendor, and financial criteria?
- Can you define the validation and approval process for this project?
- What are the primary business objectives?
- Who is going to champion this initiative?
- Who are we competing against, and why?
While these questions provide critical information to the seller, consider how they resonate from the buyer’s perspective. How many align with your needs or aid in your decision-making process for choosing software? The seller is using these questions to qualify their opportunity rather than assessing your situation with the goal of finding a solution to meet your business objectives.
As we begin to breakdown the key differences between MEDD(P)ICC and Gap Selling, stay in a buyer’s perspective.
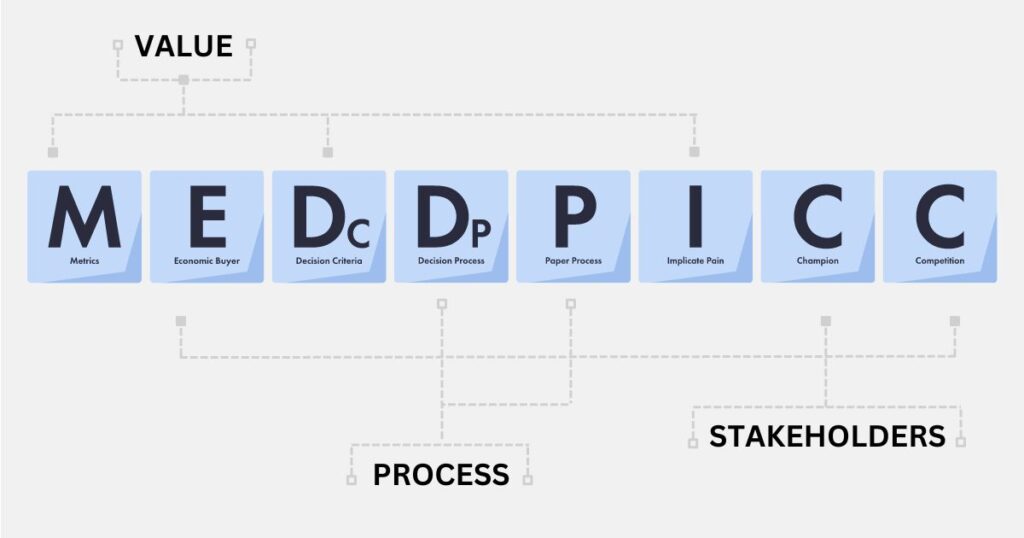
What is MEDD(P)ICC?
Developed by sales experts at PTC in the 1990s, MEDDIC, along with its’ variations MEDDICC & MEDDPICC, stands for Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision Criteria, Decision Process, Paper Process, Implication of Pain, Champion, and Competition. The framework gives sales teams a comprehensive set of categories to evaluate and qualify sales opportunities, aiming to enhance the predictability of deal closures.
What is Gap Selling?
Introduced by A Sales Growth Company and its founder, Keenan, in 2018, Gap Selling is built on the Problem-Centric™ Selling approach. It prioritizes identifying and understanding the business problems that buyers encounter. Beyond providing a structural deal management framework, Gap Selling extends in skills development, offering training in managing opportunities, leading discovery conversations, and navigating the sales cycle effectively.
Differences between MEDD(P)ICC and Gap Selling
Deal Management Vs. Sales Training
The core distinction between MEDD(P)ICC and Gap Selling is their primary focus. MEDD(P)ICC is a deal management framework, designed to help sales teams structure and analyze their sales opportunities. Its main objective is to enable leadership to predict deal outcomes by assessing information across its categories.
Conversely, Gap Selling is a holistic sales methodology that includes deal management as one of its components. It extends its’ learning beyond deal management to offer in-depth training in opportunity qualification, discovery techniques, and change management psychology.
Think of driving. The sales methodology is the car, MEDDIC, and its various spinoffs, are your blind spot detection system. It is the tools and functions that help prevent crashes. The methodology is what physically gets you from point A to point B. One is capable of getting you to the destination without the other, one is not. It is a helpful tool but you can complete the task without it.
What is Deal Management?
Deal management is the systematic approach to managing sales opportunities. It is designed to help sales teams structure, track, and analyze their deals effectively. Its objective is to address challenges sales teams face like inaccurate forecasting, long sales cycles, unexpected deal losses, and inconsistencies in deal progression. A well-implemented deal management strategy ensures sales teams can assess the viability of each deal accurately. Ultimately, deal management enhances the effectiveness and efficiency of a team to move deals through the funnel ensuring more opportunities are converted into sales.
This is where MEDD(P)ICC shines. It was designed as a deal management structure and has been distorted over the years into it’s current, common, incorrect understanding. MEDD(P)ICC does not, and has never, included skills training intended to improve a seller’s ability to move a deal through a sales cycle. It is only a deal management framework, intended to highlight blind spots in information critical to the sale.
3 Major Questions Buyers Need to Answer:
There are 3 questions every buyer is trying to answer during a sales cycle, whether it is subconscious or conscious:
- Decision 1: Should I change at all?
- Decision 2: Should I change with you?
- Decision 3: How do I change with you?
MEDD(P)ICC leans in heavily on Decision 3. This is where Economic Buyer and Paper Process are important pieces of a deal management framework. However, 80% of the sale happens in the first 2 decisions. Without knowing why a buyer should change, if they should change with you, and the metrics highlighting the cost of inaction, buyers are more likely to stand pat and make no change at all. Decision 1 and 2 are influenced and answered with Gap Selling’s Diagnostic Fields.
Gap Selling relies heavily on the diagnostic fields. These areas are critically important to dissect and comprehend the buyer’s problem environment. As a methodology, Gap Selling works with the sales team to define the metrics that are the most important to the buyer’s problem environment and thus, their willingness to change. MEDD(P)ICC leaves metric definitions to sales leadership. Both agree that the metrics are an important aspect of the sales process, however, only Gap Selling has a process in place to define these metrics. These diagnostic fields include Problem, Impact, and Root Cause.
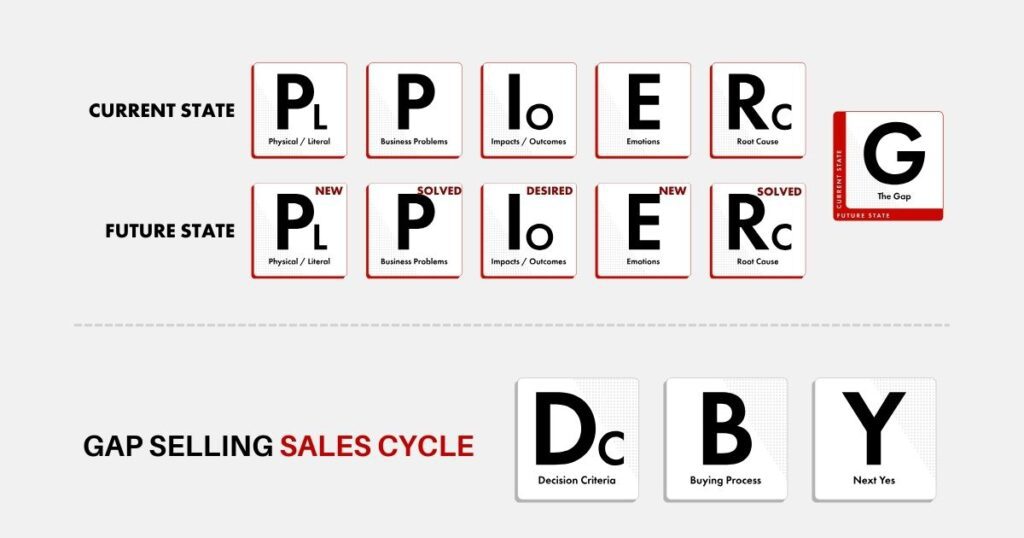
Problem, Impact, and Root Cause
Gap Selling’s 3 primary diagnostic fields are Problem, Impact, and Root Cause. These 3 fields are what builds the “gap” in Gap Selling.
The problem is the overarching business problem. Buyers start searching for a solution for a technical problem but they buy and remain customers when their business problems and impacts are alleviated.
The impact is the measurable effect of how the business problem is manifesting in the organization. Like a ripple effect.
The root cause is the technical problem, broken process, or inadequate tool that the buyer is looking to fix.
Deal Management and Diagnostic Field Results
Integrating a solid deal management strategy with a comprehensive methodology and thorough diagnostic fields is what elevates sales performance. Having captured and analyzed the information outlined in the Gap Selling framework, sales teams have seen improvements in forecast accuracy, close rates, and average deal size.
Opportunity Scoring
Gap Selling introduces a deal scoring system through Noted Analytics, which allocates points based on both the completeness and quality of data in each CRM field. This approach offers a data-driven method to evaluate the health of each deal, offering a transparent view of pipeline conditions. It helps in early identification of potential issues or areas of concern within the sales cycle, allowing for timely intervention.
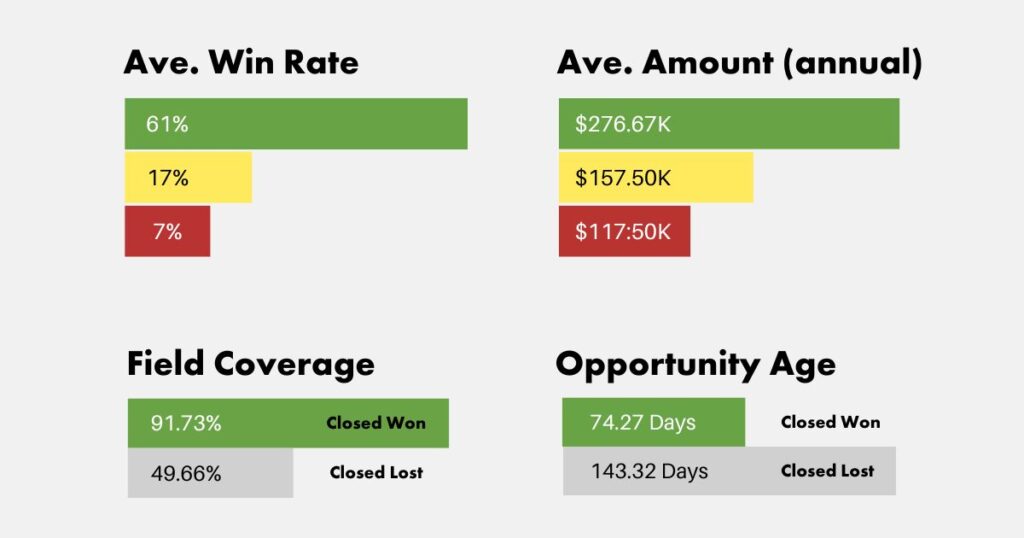
Close Rates and Deal Values
Data from organizations utilizing Gap Selling indicates that deal with comprehensive or near complete alignment with the diagnostic fields boast a win rate of 61%, significantly higher than the 17% win rate for deal with significant holes in field coverage. Moreover, deals with complete diagnostic field coverage record an average deal size of $276,670, again, significantly higher than the $157,500 average for deals with insufficient data.
Closed-won deals have an average field coverage rate of 91.73% in contrast to closed-lost deals with an average field coverage rate of 49.66%. The duration of the sales cycle also differs, with closed-won deals lasting 74.27 days and closed-lost 143.32 days.
With both comprehensive sales training and deal management, the results are clear. By prioritizing information collection, structure opportunity management, and data-informed decision-making sales teams are able to push through performance benchmarks and set a new standard for efficiency and success.
In short, measuring the business Gap in Gap Selling’s formal structure contains the strongest predictive indicators for a win.



0 Comments